Working in confined spaces can be challenging. It is even more challenging when there’s extreme heat involved. Confined spaces with high heat levels can create a hazardous and risky work environment. This extends beyond just the physical discomfort caused by heat. Heat can make it harder for workers to breathe properly, lead to dehydration, and pose a significant risk of heat stroke.
What are Confined Spaces?
Before going further, it is essential to understand the definition of confined spaces. Confined spaces are areas that are not designed to accommodate human beings but are occasionally used for work purposes. These places are typically small, cramped, poorly ventilated, and may present potential hazards to workers required to enter them. Common examples of confined spaces in the workplace include sewers, tanks, manholes, crawl spaces, and vessels. They are often dimly lit, and the internal environment can be life-threatening as it can trap and injure the workers within.

Confined Spaces Hazards
The most common hazards associated with confined spaces include:
- Lack of oxygen: Confined spaces are typically poorly ventilated, resulting in inadequate oxygen levels. This can cause the accumulation of toxic gases such as methane, carbon monoxide, and hydrogen sulfide.
- Flammable materials: Confined spaces may contain flammable materials, posing a risk of an explosion. These materials can build up and explode when exposed to an ignition source.
- Health-hazardous substances: Confined spaces may contain hazardous substances, such as chemicals or asbestos, which can lead to debilitating health problems or diseases.
What is Heat Stress?
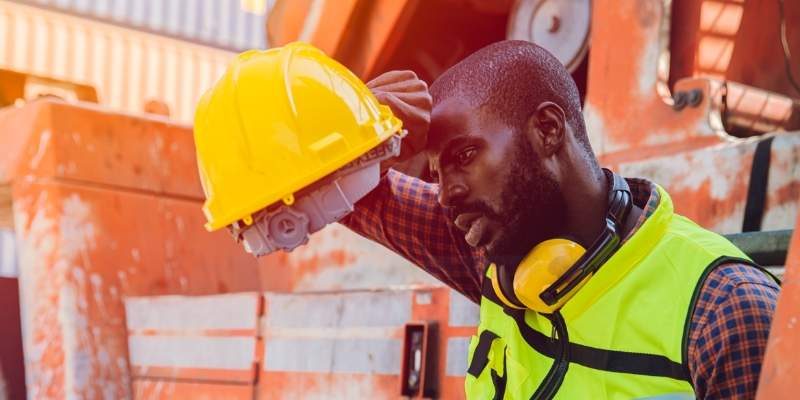

Heat stress is a condition that can occur when the body is exposed to high temperatures for extended periods. The body struggles to regulate its temperature and cool itself down. As the body temperature rises, workers may feel disorientated, lethargic, and nauseous. If left untreated, heat stress can progress to heatstroke, which can be fatal.
Working in confined spaces can make heat stress even more dangerous due to the limited space, making it challenging to move, breathe properly, and escape the heat. It is crucial to conduct heat assessments in confined spaces and take proactive measures to reduce the risk of heat stress.
Preventing and Managing Heat Stress in Confined Spaces
Employers can implement various preventive measures to reduce the risk of heat stress in enclosed spaces. These measures include:
- Conducting heat stress assessments in the confined spaces.
- Training workers to identify and report heat stress symptoms.
- Installing air-conditioning and ventilation systems to keep the air circulating and dissipate heat.
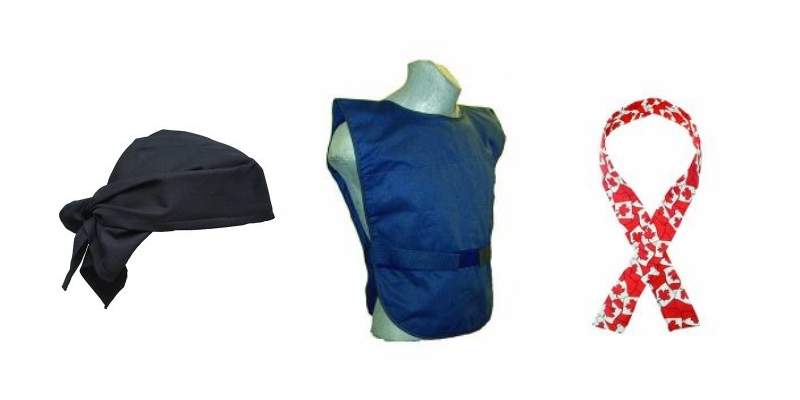
- Providing workers with personal protective equipment, such as brimmed hard hats, sunscreen, protective cooling apparel, and breathable clothing to help regulate body temperature.

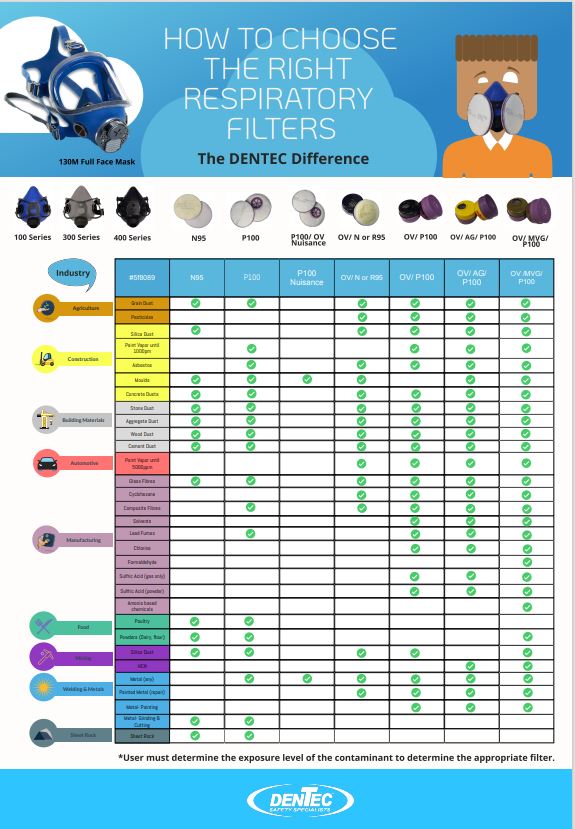
- Providing workers with respiratory protection to protect against hazardous substances. Once it has been determined that the confined space is safe to enter, and appropriate controls are in place, workers can proceed with their work. In cases where the confined space is a metal tank or container, the typical work involves resurfacing the inside of the space. This often involves activities such as grinding, cutting, welding, and painting. It is important to note that different respiratory hazards require varying levels of protection. Be sure to use Dentec’s Guide to Choosing the Right Respiratory Filters for the job.
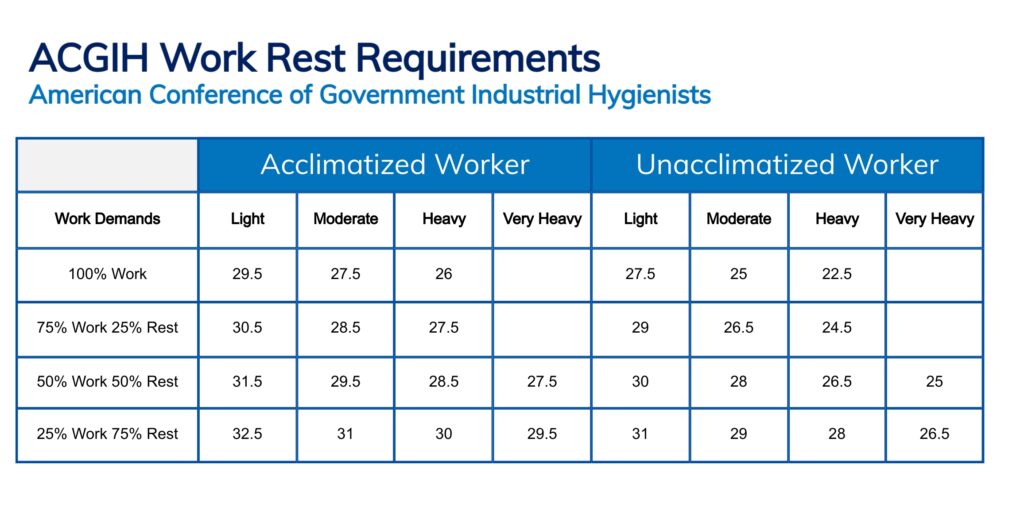
- Scheduling breaks for workers to rest and cool off. Refer to the American Industrial Hygiene Association recommended “Work Rest Ratio” guidelines for working in hot environments.
- Implementing a rehydration program for employees. Hydration safety works best with formulas designed specifically for industrial workers, featuring low sodium and sufficient potassium, two key electrolytes necessary for proper hydration in the workplace.
Consider hydration solutions like the great-tasting scientifically formulated electrolyte replacement activity drink, Sqwincher.

Employers should also have an emergency action plan that outlines the steps to take in case an employee is affected by heat stress or another heat-related illness.
The Bottom Line
Working in confined spaces poses a significant risk, especially during hot weather. Employers must put measures in place to reduce these risks for their employees. These measures must be implemented, enforced, and all employees must receive proper training on methods to keep themselves cool and safe while working in confined spaces.
Ultimately, the goal is to ensure that the workers are healthy, safe, and comfortable while working in the confined spaces. This will go a long way in reducing the risk of heat stress, accidents, and injuries.
Helpful Resources
- Heat Stress Facts
- 3 Ways to Beat Heat Stress and Stay Safe
- Heat Stress Training Poster
- Choosing the Right Respiratory Protection
- Hydration in the Workplace: How to Make the Right Choice
Dentec Safety is a leading manufacturer and distributor of safety products in the North America since 2004. Dentec Safety is dedicated to providing the highest quality safety products and solutions delivering enhanced value and comfort. Our expertise from decades of experience in Industrial Safety and our innovative design technologies have solidified us as thought leaders in the field. Protection and comfort are at the core of everything we do at Dentec. As a leading manufacturer of Safety Solutions, it is our mission to help organizations do the right thing, keep their employees safe and exceed Industry Health & Safety Standard.








